Sentimental Analysis
The project is about extracting sentiments from user comments from movie reviews. The comments are divided into two classes of positive and negative comments
Introduction
This project aims to build a sentiment analyzer of movie reviews provided by the user. The system would classify user review into two categories namely Positive and Negative. This project focuses on the pre-processing part and try to find the best word embedding for movie reviews. There are several models available to embed words into high dimensional vectors, however for this project skim gram model was chosen to produce word embeddings. Corpuses of different types were used,and model parameter were tuned to find optimal word embeddings.
Preprocessing
Preprocessing is crucial step for any machine learning system. Pre processing helps in optimization of computation process by removing unwanted data, and representing it in a way that it could be processed and evaluated efficiently.
Stemming
For grammatical reasons, reviewers use different forms of a word, such as ‘study’ and ‘studying’. Furthermore, there are families of derivationally related words with similar meanings, such as democracy, democratic, and democratization. In many situations, it seems as if it would be useful for a search for one of these words to return documents that contain another word in the set.
To serve this purpose we use Stemming which is a process of reducing inflected (or sometimes derived) words to their original word stem. It attempts to remove the differences between inflected forms of a word, in order to reduce each word to its root form. For instance, foxes may be reduced to the root fox, to remove the difference between singular and plural in the same way that we removed the difference between lowercase and uppercase. Stemming is a computationally efficient technique of reducing derived words to their root from. In the language like English the word forms are changed by adding suffix or prefix to the root word. Creating token (explained below) for root word rather than all the derived forms concentrates the probability mass on the root word and makes it easier to analyze the similarity of word vectors. The root doesn’t have to be a real word because as long as the same terms are produced while Stemming and while searching the purpose is served.
Tokenization
Digital text is usually a sequence of characters or words or phrases. To do any kind of real processing on this text we have to pre-process this text into segmented linguistic units such as number, words, punctuations, alpha-numeric. This process is called tokenization.
Tokenization is an essential preprocessing part of NLP systems. Generally, tokenization is defined as the process of breaking up the given text into units called tokens. Commonly, complete sentences or words are converted into tokens. Token could be generally created using stemmed words or could be specialized according to the application. A Tokenizer algorithm would convert sentence like ‘Friends, Romans, Countrymen, lend me some money’ into list of tokens ‘Friends’, ’Romans’, ’Countrymen’, ’lend’, ’me’, ’some’, ’money’.
These tokens can be referred as terms or words, but it is sometimes important to make a type/token distinction. A token is an instance of a sequence of characters in some particular document that are grouped together as a useful semantic unit for processing. The important thing to keep in mind for tokenization phase is how exactly are tokens generated from a piece of text. In the example above, it looks very trivial as we just break the sentence on whitespace and then we remove any punctuation. This approach is good as a starting point but is not very generalizable over large texts. Also, it depends on the language of corpus, but even in English there can be a lot of tricky cases, hence the process should always be considered based on the task at hand.
Stop words and special characters
The corpus use some common words in the sentences which are not required for the analysis. Words like ‘of’, ‘is’, ‘to’, are known as stop words and should be pruned from the corpus after converting it into tokens. Some special characters like ‘*’, ‘#’ and ‘@’, are also removed from the tokens before further processing.
Furthermore, there is a special case for hyphenated words. These words can be a single word means one token or can be divided into two or more. These hyphenated parts of text present a case of ambiguity for a tokenizer-sometimes a hyphen is part of a token, i.e. self-assessment, F-15, forty-two and sometimes it is not e.g. Los Angeles-based. Tokenization of hyphenated words is again task dependent.
Skip Gram Model
Skip gram model is a simple neural network with a single hidden layer. Unlike usual neural networks the model is not used for prediction of classes, it is used to learn weights, the weights are than used as word vectors to embed words in high dimension.
The dictionary of words is selected which should contain all the possible words available in the corpus. The words in the corpus are than mapped as one-hot representation vector. The hidden layer of neural network has units equal to the number of dimensions of word vector. The output layer again has units equal to the length of one-hot vector. Figure below shows an example of neural network design for skip gram.
The design described above is computationally expensive and does not end in reasonable time for large dictionary and large corpuses. Therefore, some techniques are used to reduce the learning time of the network. The words which are below a certain threshold in the corpus are ignored, these words commonly do not contribute in the final result as they are rarely used. Furthermore, the words are concatenated into phrases like ‘New’ and ‘York’ is converted into phrase ‘New York’. The stop words like ‘in’ and ‘the’ are removed from the corpus (preprocessing) before training the model.
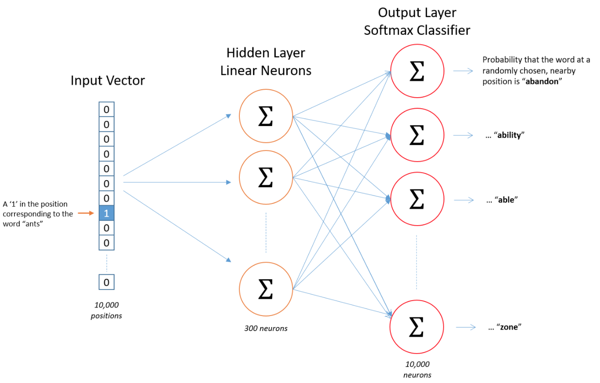
Moreover, given a specific word in the middle of a sentence (the input word), the “closer” words are looked upon and one is picked at random. The network calculates the probability for every word in vocabulary of being the “closer” that is selected. This closeness is actually controlled by a “window size” parameter to the algorithm. A typical window size might be 5, meaning 5 words behind and 5 words ahead (10 in total).
We’re going to train the neural network such that the output probabilities are going to relate to how likely it is to find each vocabulary word nearby our input word. For example, if you gave the trained network the input word “Soviet”, the output probabilities are going to be much higher for words like “Union” and “Russia” than for unrelated words like “watermelon” and “kangaroo”.
Neural Network
The method used for sentimental analysis consist of class of neural network known as RNN. RNNs are a class of neural networks that takes into account the input at each time step and computes a hidden state vector.A Long Short-Term Memory network (LSTM) is a variant of RNNs that performs better when the output at time t depends on the earlier inputs. The network of RNN consist of multiple LSTM cells. Each LSTM cell consist of three gating units namely, an input gate, a forget gate, and an output gate. The activation function used in the mentioned gates is sigmoid function.
Model Evaluation
In previous sections, we discussed about components of system and the configuration used in this system. In this section, we discuss the training and testing data used and how we quantitatively evaluate the quality of word vectors produced.
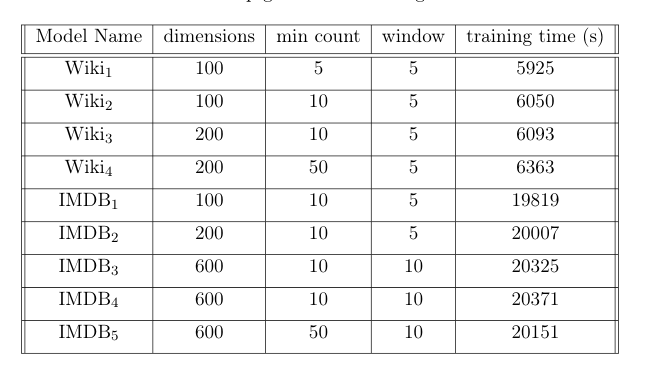
In this project we decided to test two kinds of corpus for learning word vector representation. One of the corpus was a generic corpus, taken from Wikipedia. The other one was the dump of IMDB reviews consisting of equal number of positive and negative reviews. The corpuses were tokenized using the preprocessing techniques described above. The tokenized results were fed into the neural network to learn the weights. The parameters of the network described above were changed to create different representation of the words and evaluate which one best suits the purpose of sentimental analysis. Table below shows the models created for evaluation
Intrinsic Tests
Intrinsic evaluation of word vectors is the evaluation of a set of word vectors generated by Word2Vec on specific intermediate subtasks (such as word similarity). These subtasks are simple and fast to compute and help in understanding the system used to generate the word vectors. An intrinsic evaluation should typically return to us a number that indicates the performance of those word vectors on the evaluation subtask.
There are several types of intrinsic tests used but they are commonly categorized into following categories
Correlation Evaluation
One popular way to evaluate the quality of generated word vectors is by comparing the similarity word vectors with the predefined set of similar words available. More formally, this correlation is a statistical measure that describes the association between words. The method we use for calculating the correlation is based on measuring different type of strength of association between two words. The comparison word set could be generic or application specific.
For this application we want to classify reviews into two classes, therefore we collected sample of good words and bad words commonly used by the movie reviews. Table below shows the positive and negative words
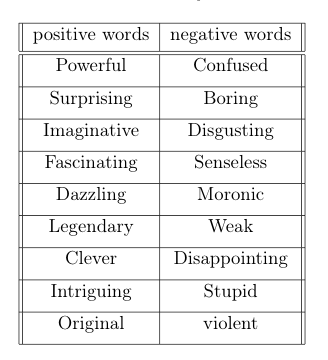
The correlation between the top 10 bad words and good words was performed with the words shown in above table. The figure below shows the result of top 4 models. Top-left: IMDB1, Top-right: IMDB5, Lower-left: Wiki2, Lower-right:Wiki3
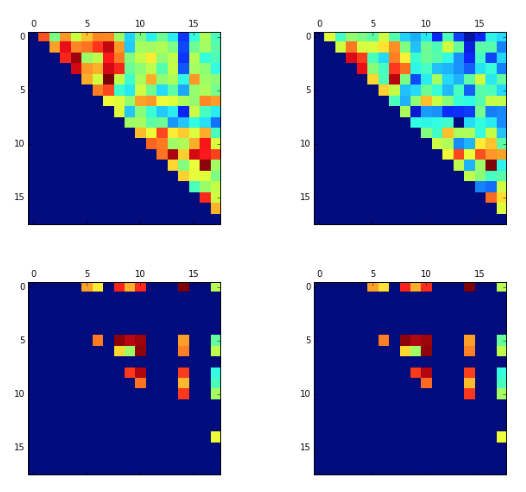
Furthermore, to check the similarity of the words most similar to good and bad were checked for the selected models. It could be seen that IMDB models have more relevant words. However, it should be noted that the similarity ranged from 95% to 85% for Wiki models, whereas for IBDM it ranged from 78% to 64%.
Word Vector Analogies
Another popular choice for intrinsic evaluation of word vectors is its performance in completing word vector analogies. The example for vector analogies would be queen – king = actress – actor.
A subset of benchmark test set of Google consisting of 20,000 syntactic and semantic test examples was used for all the 4 models mentioned above. The table below shows the results
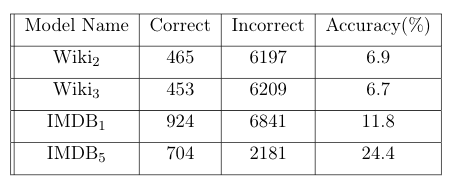
The results show clearly that IMDB models are much better in recognizing the analogies than Wiki models.
Categorization
Categorization is another popular way used by the evaluate the quality of generated word vectors, the goal is to recover a clustering of words into different categories. To do this, the corresponding word vectors of all words in a dataset are clustered and the purity of the returned clusters is computed with respect to the labeled dataset. The Figure below shows the clustering of 4 models selected. Top-left: IMDB1, Top-right: IMDB5, Lower-left: Wiki2, Lower-right:Wiki3
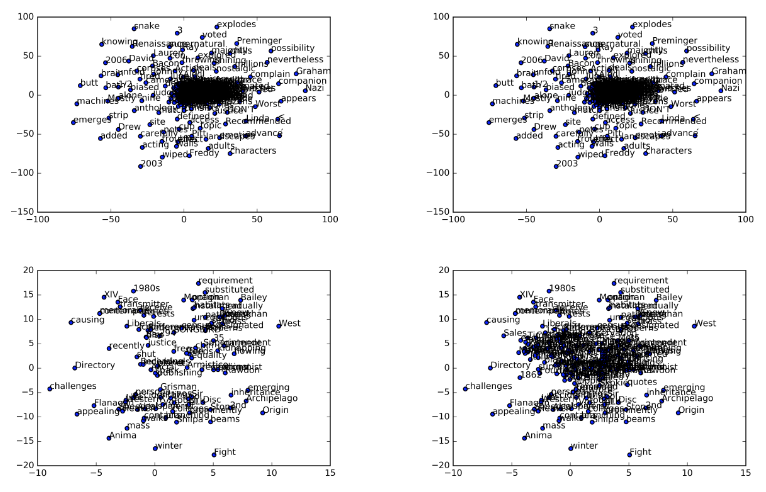
The models were also tested with clustering capacity and it was found that Wiki corpus have clusters more related to world war and Allies but there were not much word clusters representing the good or bad quality. Whereas in the IMDB models’ there is a huge cluster of words in the center and there are some small clusters representing some type of positivity and negativity.
Extrinsic Evaluation
The neural network with cell type of LSTM was used to classify reviews into two classes. The accuracy of neural network was used to evaluate the word vector embedding. Because of the time taken to train the model only one model was selected to be tested on the LSTM. We chose IMDB1 on the basis of intrinsic evaluation.
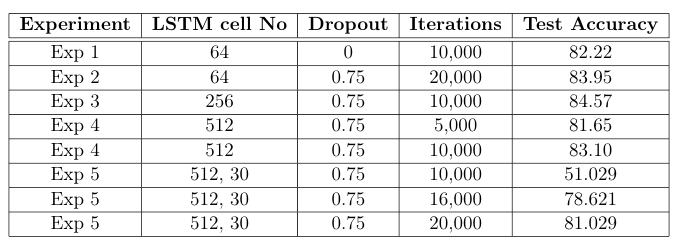
We conducted 5 experiments to find the optimal setting for neural network. The first experiment was conducted as a baseline experiment; with one layer of 64 LSTM cells, batch size set to 24 and no dropout. Different optimizer algorithms were tried on the baseline design, including stochastic gradient descent, Momentum and Adam. Based on the results, it was decided that Adam should be used in the future experiments. The learning rate of the algorithm was set to 0.001, whereas the values of beta1 and beta2 were set to 0.9 and 0.999 respectively. The network was trained for 10,000 iterations, as expected the results of this model were not good. To improve the accuracy of the design we changed the hyperparameters of the model. In second experiment dropout of 0.25 was introduced and the number of iterations were set to 20,000. In following experiments the number of LSTM cells were increased by the multiple of 2 (i.e: 256 and 512). The increase in LSTM cells required more iterations to stabilize so the number of iterations were increased to 30,000. Early stopping was introduced in these models, so that they do not overfit the training set. As the last experiment the layers of the model were increased to 2, the first layer consisted of 512 LSTM cells, this layer was connected to 30 LSTM cells and a dropout of 0.75 was introduced in the second layer.
The trained models were then tested on the test data. The results of the models are shown in Table below. The results indicate that Experiment 3 gives the highest test accuracy for the given dataset.
Conclusion
In this project we tried to evaluate the word2vec representation of different corpuses using both intrinsic and extrinsic evaluation. We tried different popular intrinsic test to find the best embedding suitable for our application. We than fed the selected embedding into neural network and tuned the neural network to find the optimal hyper parameters. The accuracy achieved by the neural network is pretty decent.
The code for this project could be found here